Unveiling the Hidden: Pancreas Vanishes Amid Bowel Gas!
17/09/2023
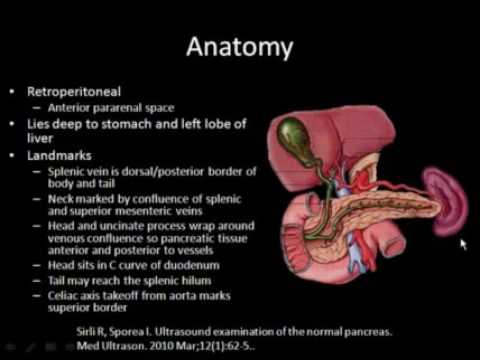
The pancreas, a vital organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and regulating blood sugar levels, can sometimes be difficult to visualize due to bowel gas. This phenomenon, known as pancreas obscured by bowel gas, poses a significant challenge for medical professionals when diagnosing pancreatic diseases and conditions. The presence of excessive gas in the bowels can hinder the accuracy of imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, making it harder to detect abnormalities in the pancreas. This article aims to explore the causes and implications of pancreas obscured by bowel gas, as well as the potential solutions and alternative imaging methods that can aid in overcoming this obstacle. A better understanding of this issue will not only improve diagnostic accuracy but also contribute to more effective management and treatment strategies for pancreatic disorders.
- Pancreas obscured by bowel gas refers to a medical condition where the visibility of the pancreas is reduced due to the presence of gas in the bowels.
- This condition can make it challenging for medical professionals to accurately diagnose pancreatic diseases or abnormalities using imaging techniques like X-rays or ultrasounds.
Advantages
- Accurate diagnosis: When the pancreas is obscured by bowel gas on imaging scans, it can sometimes be challenging to accurately diagnose pancreatic conditions. This may lead to a more comprehensive evaluation of the patient, including further tests and examinations, which can help identify other potential causes or underlying issues that may be contributing to the symptoms. This thorough evaluation can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the patient's overall health and assist in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
- Avoid unnecessary interventions: In cases where the pancreas is obscured by bowel gas, medical professionals may choose to avoid invasive interventions or procedures that could potentially harm the patient. This cautious approach ensures patient safety and reduces the risk of complications. By refraining from unnecessary interventions, medical practitioners can adopt a more conservative management strategy, focusing on non-invasive treatments or alternative diagnostic methods, while closely monitoring the patient's condition. This approach minimizes potential harm and allows for a more individualized and patient-centered care approach.
Disadvantages
- Difficulty in diagnosing pancreatic conditions: When the pancreas is obscured by bowel gas, it becomes challenging for medical professionals to accurately diagnose pancreatic conditions. This can lead to delayed or incorrect diagnoses, potentially affecting patient outcomes.
- Increased risk of complications during surgical procedures: If the pancreas is obscured by bowel gas during surgery, there is an increased risk of complications. Surgeons may find it harder to visualize and maneuver around the pancreas, potentially increasing the risk of accidental injury to the organ or surrounding structures.
- Limited effectiveness of imaging techniques: Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans may be less effective in visualizing the pancreas when it is obscured by bowel gas. This can make it harder to identify abnormalities or monitor pancreatic diseases, leading to limited diagnostic accuracy and potentially impacting treatment decisions.
What is the meaning of bowel gas in the pancreas?
In the context of acute pancreatitis, the presence of intrapancreatic gas is typically associated with infection caused by gas-forming organisms. Computed tomography (CT) scans are useful in diagnosing pancreatitis, evaluating its severity, and identifying any complications. The visualization of gas within an inflamed pancreas suggests the formation of an abscess, which often necessitates surgical intervention. Understanding the significance of bowel gas in the pancreas aids in recognizing the need for appropriate medical management and potential surgical procedures.
The presence of intrapancreatic gas in acute pancreatitis indicates infection by gas-forming organisms. CT scans are valuable for diagnosing and assessing the severity of pancreatitis, as well as identifying complications. The visualization of gas in the inflamed pancreas suggests the development of an abscess, often requiring surgical intervention. Recognizing the significance of bowel gas in the pancreas helps determine appropriate medical management and potential surgical procedures.
In certain instances, the visibility of the pancreas through ultrasound may be hindered due to the presence of gas in the stomach and duodenum. Although ultrasound is typically effective in identifying the pancreas, the obstruction caused by bowel gas can obscure its visibility. Despite attempts to enhance visibility through the administration of orally consumed fluids, such as water, suboptimal results have been observed. Therefore, it is important to consider alternative techniques or approaches when examining the pancreas in cases where bowel gas may be a frequent occurrence.
The presence of gas in the stomach and duodenum can hinder the visibility of the pancreas during ultrasound. Despite attempts to improve visibility with orally consumed fluids, suboptimal results have been observed. It is crucial to explore alternative techniques or approaches when examining the pancreas in cases where bowel gas is common.
What is the definition of "obscured by bowel gas"?
"Obscured by bowel gas" refers to the presence of intestinal gas that obstructs or conceals other structures during an ultrasound examination. This can impede a doctor's ability to thoroughly examine organs and tissues. Excessive gas can arise from various factors, such as consumption of high-fiber foods or carbonated drinks. Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of overlying bowel gas is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective medical treatment.
Excessive bowel gas can hinder the effectiveness of ultrasound examinations by obstructing or concealing other structures. This can make it difficult for doctors to thoroughly examine organs and tissues. Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of excessive gas is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective medical treatment.
Unveiling the Mystery: How Bowel Gas Affects Pancreatic Visibility
The presence of bowel gas can significantly impact the visibility of the pancreas, making it a challenging task for radiologists to accurately diagnose certain pancreatic conditions. Bowel gas can obscure the pancreas on imaging studies, leading to potential misinterpretation and missed diagnoses. It is crucial for radiologists to be aware of this phenomenon and employ various techniques to minimize its effect. By utilizing specific imaging protocols, patient positioning, and adjusting technical parameters, radiologists can enhance pancreatic visibility, ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective treatment strategies for patients.
The presence of bowel gas can make it difficult for radiologists to accurately diagnose pancreatic conditions. It can obscure the pancreas on imaging studies, leading to potential misinterpretation and missed diagnoses. Radiologists must be aware of this and use specific techniques to minimize its impact, ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective treatment strategies for patients.
The Intricate Relationship Between Bowel Gas and Pancreatic Obscurity
The intricate relationship between bowel gas and pancreatic obscurity is a topic that continues to baffle researchers in the medical field. The presence of excessive bowel gas can often lead to difficulties in diagnosing pancreatic conditions, as the gas can hinder the visibility of the organ during imaging tests. This creates a challenge for physicians in accurately identifying and treating pancreatic disorders. Further studies are needed to understand the mechanisms by which bowel gas affects pancreatic clarity, potentially leading to improved diagnostic methods in the future.
The relationship between bowel gas and pancreatic obscurity remains a perplexing topic for medical researchers. Excessive bowel gas can impede the diagnosis of pancreatic conditions, as it obstructs visibility during imaging tests. Accurate identification and treatment of pancreatic disorders pose a challenge for physicians. Further research is necessary to comprehend the mechanisms by which bowel gas impacts pancreatic clarity, potentially leading to enhanced diagnostic techniques in the future.
Exploring the Consequences of Bowel Gas on Pancreatic Imaging
When it comes to pancreatic imaging, the presence of bowel gas can have significant consequences. Bowel gas can create artifacts that mimic or obscure pancreatic lesions, making accurate diagnosis and interpretation challenging. It can also cause image distortion, affecting the overall quality of the images obtained. Additionally, the presence of bowel gas can hinder the visualization of the pancreas, leading to potential missed diagnoses or delays in treatment. As a result, it is crucial for radiologists and healthcare professionals to be aware of the impact of bowel gas on pancreatic imaging and take necessary measures to minimize its effects.
The presence of bowel gas during pancreatic imaging can have significant consequences. It can create artifacts that mimic or obscure pancreatic lesions, distort images, and hinder visualization of the pancreas. Radiologists and healthcare professionals must be aware of these effects and take measures to minimize their impact for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
Decoding Pancreatic Obscurity Caused by Bowel Gas Build-up
Pancreatic obscurity, often overlooked, can be a result of bowel gas build-up. This elusive condition occurs when excessive gas accumulates in the bowels, pressing against the pancreas and causing discomfort. The symptoms may mimic other gastrointestinal issues, making it challenging to diagnose accurately. Patients experiencing prolonged abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements should seek medical attention. Specialized diagnostic tests, such as CT scans and ultrasounds, can help identify the underlying cause. Early detection is crucial in managing pancreatic obscurity and preventing further complications.
Often overlooked, pancreatic obscurity can be a result of excessive bowel gas. This condition, characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and irregular bowel movements, can be challenging to diagnose accurately. Specialized diagnostic tests like CT scans and ultrasounds are crucial for early detection and preventing complications.
In conclusion, the presence of bowel gas obscuring the pancreas can pose a significant challenge in diagnosing and evaluating pancreatic abnormalities. The difficulty lies in accurately identifying and differentiating between normal gas-filled structures and potential pathological findings. Utilizing advanced imaging techniques such as contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help overcome this obstacle by providing clearer visualization of the pancreas. Additionally, the use of specific protocols, including patient preparation and positioning, can minimize the interference of bowel gas and improve diagnostic accuracy. Although pancreas obscuration by bowel gas remains a complex issue, advancements in imaging technology and techniques continue to enhance our ability to accurately assess pancreatic pathologies and provide timely intervention. Efforts should be made to further explore and refine these methods to ensure accurate diagnosis and management of patients with pancreatic diseases.
